ist-pasion.com – Jamaica, a vibrant island nation in the Caribbean, is renowned for its rich cultural tapestry, which includes a diverse and dynamic religious landscape. This article explores the various religious traditions practiced in Jamaica, highlighting how they contribute to the country’s social fabric and foster a sense of unity amidst diversity.
The Dominant Religions in Jamaica
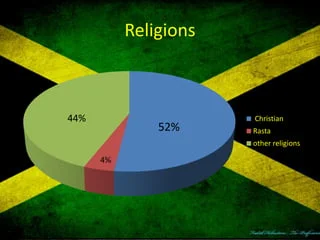
Christianity
Christianity is the predominant religion in Jamaica, with the majority of the population identifying as Christians. The Christian community is further divided into several denominations, with Protestantism being the most prevalent, including churches such as the Church of God, Seventh-day Adventist, Baptist, and Pentecostal. The Roman Catholic Church also has a significant presence on the island.
Rastafarianism
Rastafarianism, a religious movement that originated in Jamaica in the 1930s, is another key component of the country’s religious landscape. Rastafarians worship Haile Selassie I, the former Emperor of Ethiopia, as the incarnation of God, and their beliefs are centered around themes of peace, love, and unity. The movement has had a profound influence on Jamaican culture, particularly in music and social thought.
Other Religions
While Christianity and Rastafarianism are the most visible religions, Jamaica’s religious landscape also includes other faiths such as Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism. These religions are practiced by smaller but active communities, contributing to the island’s religious diversity.
Unity in Diversity
Despite the variety of religious beliefs, Jamaica’s religious landscape is characterized by a strong sense of unity. This unity is fostered through shared values such as respect, tolerance, and community. Religious festivals and events often attract participants from various faiths, promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
Challenges and Opportunities
The coexistence of different religions in Jamaica is not without its challenges. Issues such as religious stereotyping and occasional tensions between groups can arise. However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth and learning. Through education and open dialogue, Jamaicans continue to build bridges across religious divides, strengthening the social cohesion that is essential for a harmonious society.
Conclusion
Jamaica’s religious landscape is a testament to the island’s capacity to embrace diversity while fostering unity. The various religious traditions practiced in Jamaica enrich the cultural mosaic and contribute to the country’s identity. As Jamaica continues to navigate the complexities of religious diversity, the principles of respect, tolerance, and community remain the cornerstones of its social fabric, ensuring that the nation remains a beacon of unity in diversity.